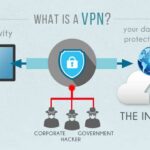
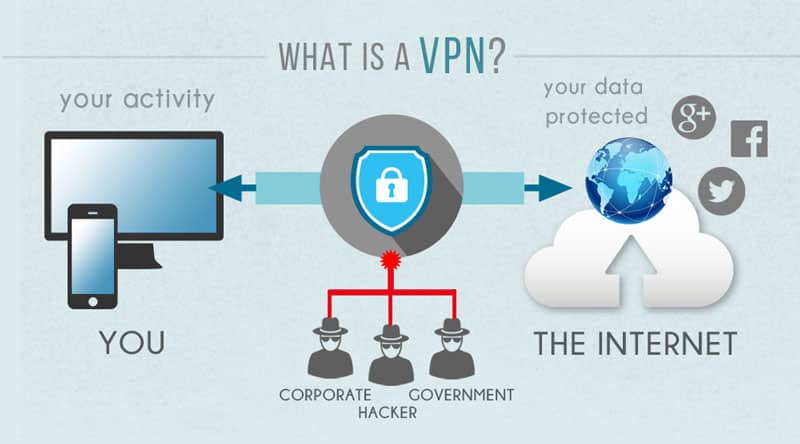
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It’s a technology that permits users to generate a secure link to another network over the internet. VPNs can access region-cramped websites, shield browsing activity from inquiring impertinently into eyes on public Wi-Fi, and supply a secure link for remote work or browsing. It authorizes users to send and receive data to the other side of shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly linked to the private network. This functionality ensures that the data transfer between the user’s device and the VPN server is encrypted, keeping it safe from malicious actors’ potential interception or manipulation. In quintessence, a VPN creates a private tunnel through which your data proceeds, shielding it from inquiries impertinently into the eyes and potential threats.
What is a VPN? And why do we use it?
This article describes the concept of VPNs, their benefits, and how they work to keep safe online privacy and security.
The Summit VPN Services of [Current Year]
An overview of the best VPN services available, comparing characteristics, pricing, and show.
How to erect and Utilize a VPN
A step-by-step escort on how to set up a VPN on numerous devices and platforms, including computers, smartphones, and routers.
Why is a VPN important?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is pivotal for several reasons, first and foremost revolving around online security, privacy, and ease of access. In an era where cyber-threatening remarks loom large and privacy be about is at the forefront of online pursuit, a VPN emerges as a censorious tool for safeguarding one’s digital existence. By encrypting internet traffic, a VPN generates a secure tunnel between a user’s device and the internet, shielding responsive to data from inquiries impertinently into eyes and potential hackers.
This encryption not only keeps safe personal information such as passwords, monetary details, and browsing history but also makes sure of namelessness by masking the user’s IP address.
Beyond security, VPNs authorize users to bypass geographical reduction and access content that may be restricted or cut in their region.
Whether it’s flow services, social media platforms, or websites, a VPN authorize
individuals to navigate the internet freely and namelessly, preserving both privacy and digital rights in an increasingly interrelated reticular world.
VPN Security: What You Require to Know
This article searches into the security aspects of VPNs, including encryption protocols, leak defense, and logging plans.
VPN Troubleshooting: Common Matter and Solutions
A guide to troubleshooting common issues with VPN links, such as slow speeds, connection drops, and like-mindedness issues.
How does a VPN work?
A VPN hides your IP address by allowing the network to alter it through a specially constructed remote server run by a VPN host. This means that if you break online with a VPN, the VPN server suits the origin of your data. A VPN works like a strainer that turns all your data into “gibberish”. Even if someone were to get their hands on your data, it would be futile.
What are the good of a VPN link?
A VPN connection dresses you up as your data traffic online and keeps safe it from external access. Unencrypted data can be viewed by anyone who has a network entrance and wants to see it. With a VPN, hackers and cyber lawbreakers can’t decipher this data.
- Encryption of your IP address: The main job of a VPN is to hide your IP address from your ISP and other third-party social gathering. This allows you to send and be given information online without the possibility of anyone but you and the VPN supplier seeing it.
- Encryption of protocols: A VPN should also stop you from departing from tracking down, for example, in the form of your internet history, search history, and cookies. The encryption of cookies is mainly important because it stops third parties from gaining access to private information such as distinctive data, monetary information, and other content on websites.
- Two-factor corroborate: By using a diversity of corroborating methods, a strong VPN checks everyone who tries to log in. For example, you might give rise to enter a password, after which a code is sent to your mobile dispatch.
- Kill button: If your VPN connection is immediately interrupted, your secure connection will also be cut in. A good VPN can detect this sudden downtime and bring to an end preselected programs, lessening the likelihood that data meet each other halfway.
History Of VPN:
The US Division of Defense was already associated with projects working on the encryption of internet transmission data back in the 1960s.
Forerunner of VPN
Their efforts led to the design of ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network), a packet-change network, which in turn guided the evolution of the Transfer Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP).
The TCP/IP had four levels: Link, internet, convey, and application. At the internet level, local networks and devices could be linked to the universal network – and this is where the risk of subjection became clear.
Early VPN
Adjacent to Singh-Pall developing PPTP, the internet was getting bigger in fashionable and the need for consumer-ready, worldly security systems came out. At that time, anti-virus schemes were already successful in stopping malware and spyware from infecting a computer system.
How many types of VPNs are there?
There are many dissimilar types of VPNs, but you should certainly
be familiar with the three main types:
- SSL VPN: Frequently not all workers of a company have entrance to a company laptop they can use to work from home. Throughout the coronavirus crisis in the Spring of 2020, many companies faced the difficulty of not having enough apparatus for their worker. In this instance, companies fall back on an SSL-VPN solution, which is usually executed via a correlate with the hardware box. The necessary condition is usually an HTML-5-have the ability to browse, which is used to call up the company’s login page.
- Site-to-site-VPN: A site-to-site VPN is basically a private network designed to hide private organization networks and allow users of these secure networks to entrance
each other’s assets.
Site-to-site VPNs are mostly used in big companies. They are complex to execute and do not offer the same pliability as SSL VPNs. However, they are the most successful way to ensure transmission within and between large divisions.
- Client-to-server VPN: Connecting via a VPN client can be visualized as if you were connecting your home PC to the company with an additional cable. The worker can dial into the company network from their home place of business via a secure connection and take action as if they were sitting in the office. However, a VPN client ought to first be installed and constructed on the computer.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, VPNs have become essential tools for continued privacy and security online. By encrypting data transference and masking IP addresses, VPNs offer users a sense of namelessness and defense from the cyber-threatening remark. Besides, they enable entrance to geo-blocked content and make possible secure remote connections for businesses and particular alike.
While VPNs are not without their restriction, such as possible slowdowns in connection speed and the need to trust the VPN service supplier, their goods far outweigh the drawbacks for numerous users.
These articles cover numerous aspects of VPN technology, its uses, and thoughts for both personal and professional use.








Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.